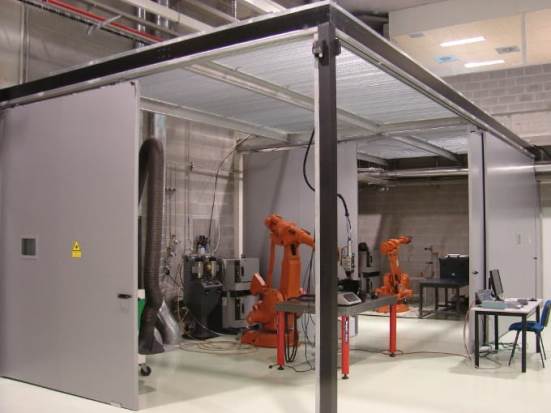
Direct laser deposition
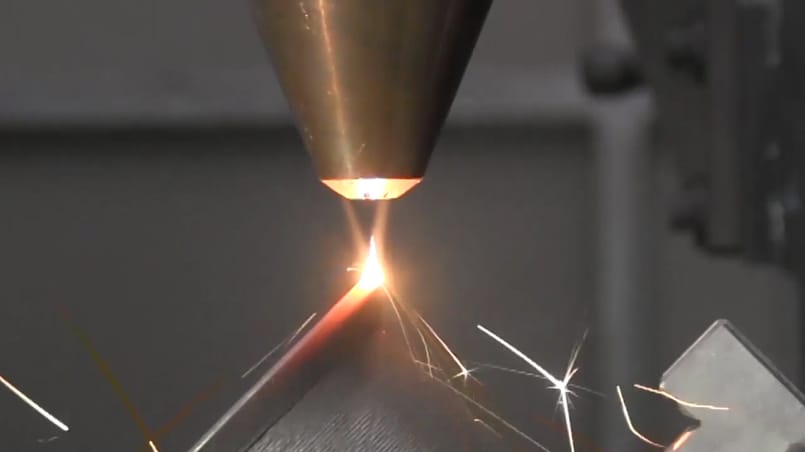
Generation of anti-wear and corrosion protection coatings as well as thermal barriers of various metal alloys, iron, nickel, cobalt, etc. using the technique of direct laser deposition.
The process of direct laser deposition or laser cladding allows, through the fusion of a filler material, usually in the form of metal powder, on the surface of a material and, by the action of a laser beam, the generation of a coating with similar or improved properties than those of the base substrate. The advantages of this method include minimum dilution, low and controllable heat input to the substrate, high processing flexibility and reduced distortion.
Compared to other conventional deposition techniques such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, plasma arc projection or HVOF (High Velocity Oxygen Fuel) projection, the technique of direct laser deposition produces coatings which are free of pores, cracks and deformations, with good metallurgical bonding with the substrate.
The technique is mainly applied to reinforcing and recovering critical areas in moulds, dies, tools, components, etc. It also allows the treatment of large areas and even the interior of pipes and ducts.






