The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are the 17 goals proposed by United Nations to achieve a sustainable future for everybody by 2030. A number of interrelated global challenges have been incorporated and are being addressed on a daily basis with regard to issues such as poverty, inequality, environmental degradation or prosperity.
Subsequent to being implemented in January 2016, we at Tekniker have placed our activities in line with each of these goals and have developed our own Smart and Sustainable Industry Model called Tekniker SustaINDustry to help companies identify key issues related to achieving economic, social and environmental sustainability.
Tekniker SustaINdustry: A Smart and Sustainable Industry model
Overall, the degree of sustainability of a company can be described as the extent to which it is able to operate over time in a changing environment characterised by a number of drivers or inductors that also represent a challenge and opportunity that must be suitably managed to guarantee its sustainability. For instance, an increase in the demand for products with a high degree of customisation, the reduction of time-to-market deadlines, digitisation, globalisation, climate and geographic changes are key elements that must be taken into account by companies whose aim is to achieve long-term sustainability.
The sustainability challenge cannot only be addressed from an economic perspective by focusing on obtaining short-term profits at any cost. In efforts geared towards proving support for industrial companies, Tekniker, a member of the Basque Research and Technology Alliance (BRTA), has developed its own Smart and Sustainable Industry Model called Tekniker SustaINdustry.
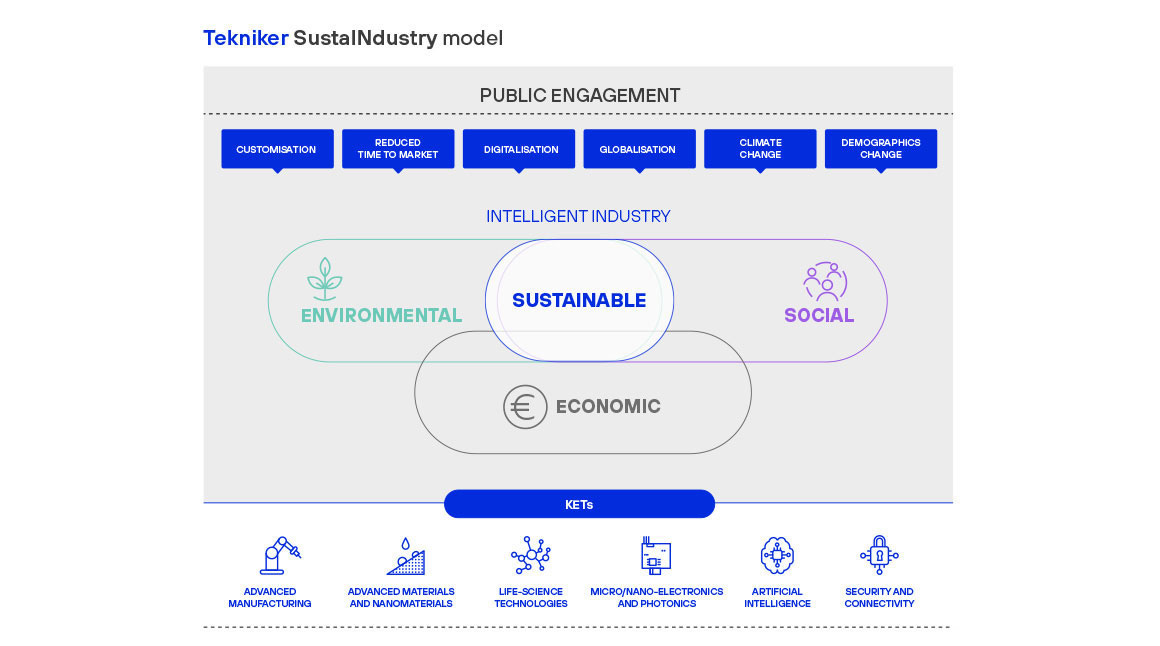
The purpose of this model is to identify the key issues to be taken into account to achieve sustainability for industrial firms and provide the necessary technological support.
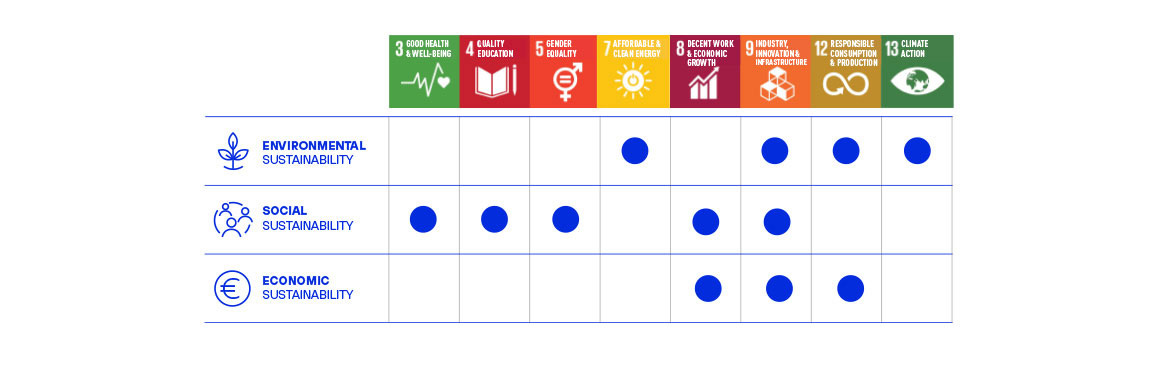
The Tekniker SustaINdustry model has estimated that, in order to achieve long-term sustainability, three key pillars must be addressed that are economic, social and environmental.
Economic sustainability
Broadly speaking, the first pillar, related to economic sustainability, refers to how important it is for a company to be profitable and competitive by guaranteeing the quality of its products and the efficiency of its processes.
Social sustainability
The second pillar, on the other hand, refers to human wellbeing. If a company sets the goal of being sustainable from a social perspective, it must retain and improve the performance of its workforce and receive the support and approval of employees, customers, associates and society at large. Consequently, new working environments will have to be adaptative, collaborative and reliable.
Environmental sustainability
Finally, the last pillar focuses on environmental sustainability. In order to achieve the 2050 climate neutrality target set for Europe, industrial firms will have to reduce their environmental impact through energy efficiency and manufacturing resources based on circular approaches such as the use of clean energy (renewables) covering entire product-service life cycles and linking different sectors and ecosystems.
